
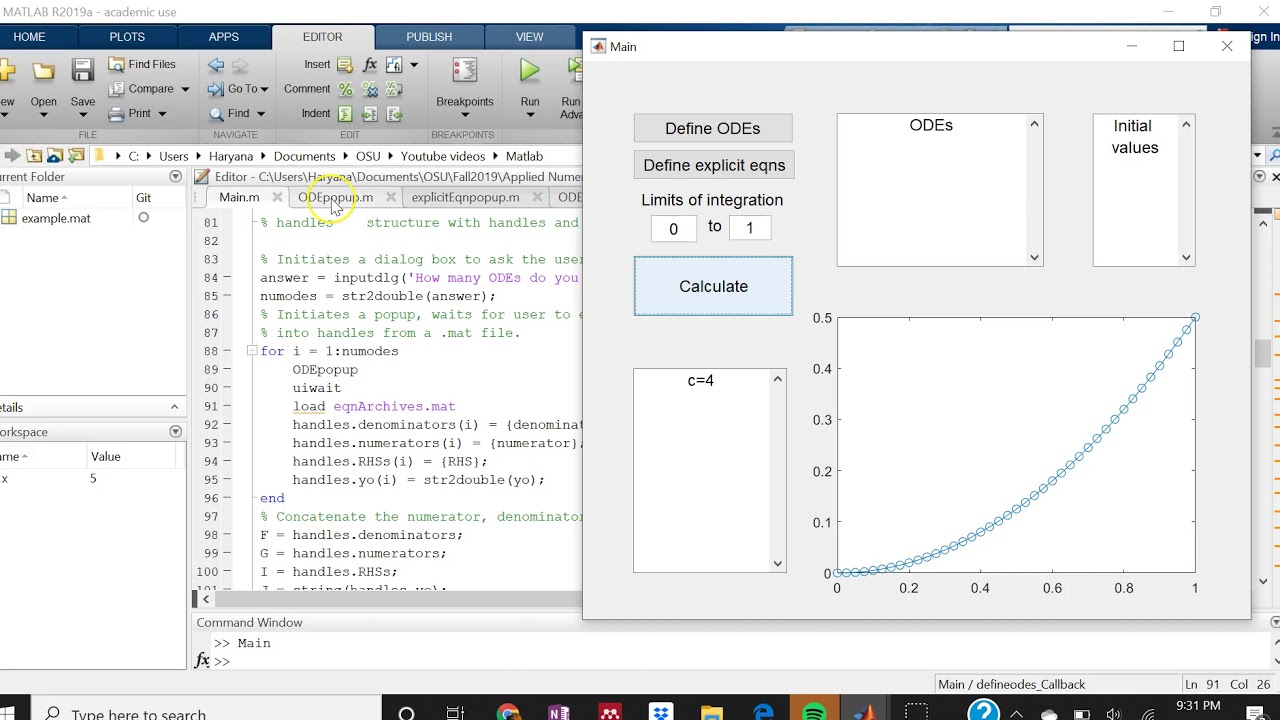
Hexadecimal notation (using uppercase letters A- F) Hexadecimal notation (using lowercase letters a- f) The more compact of %e or %f, as defined in. Tables The following tables describe the non-alphanumeric characters found in format specification strings.Ĭonversion characters specify the notation of the output.Įxponential notation (using a lowercase e as in 3.1415e+00)Įxponential notation (using an uppercase E as in 3.1415E+00) Manner, without reinitializing, through any additional matrix arguments. (columnwise) until all the elements are used up. The format string is cycled through the elements of A The fprintf function is vectorized for the case when input matrix A is The underlying C data type is a double rather than an unsigned integer.įor example, to print a double-precision value in hexadecimal, use a formatĢ. The underlying C data type is a float rather than an unsigned integer. The following non-standard subtype specifiers are supported for conversion Remarks The fprintf function behaves like its ANSI C language fprintf() namesake with certain exceptions and extensions. It can contain ordinary alphanumeric characters along with escape characters, conversion specifiers, and other characters, organized as shown below:įor more information see "Tables" and "References". The format string specifies notation, alignment, significant digits, field width, and other aspects of output format. See fopen for more information.) Omitting fid from fprintf's argument list causes output to appear on the screen, and is the same as writing to standard output ( fid = 1) fprintf( format,A.) (It may also be 1 for standard output (the screen) or 2 for standard error. Argument fid is an integer file identifier obtained from fopen.
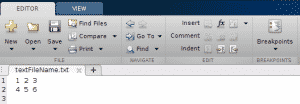
fprintf returns a count of the number of bytes written.
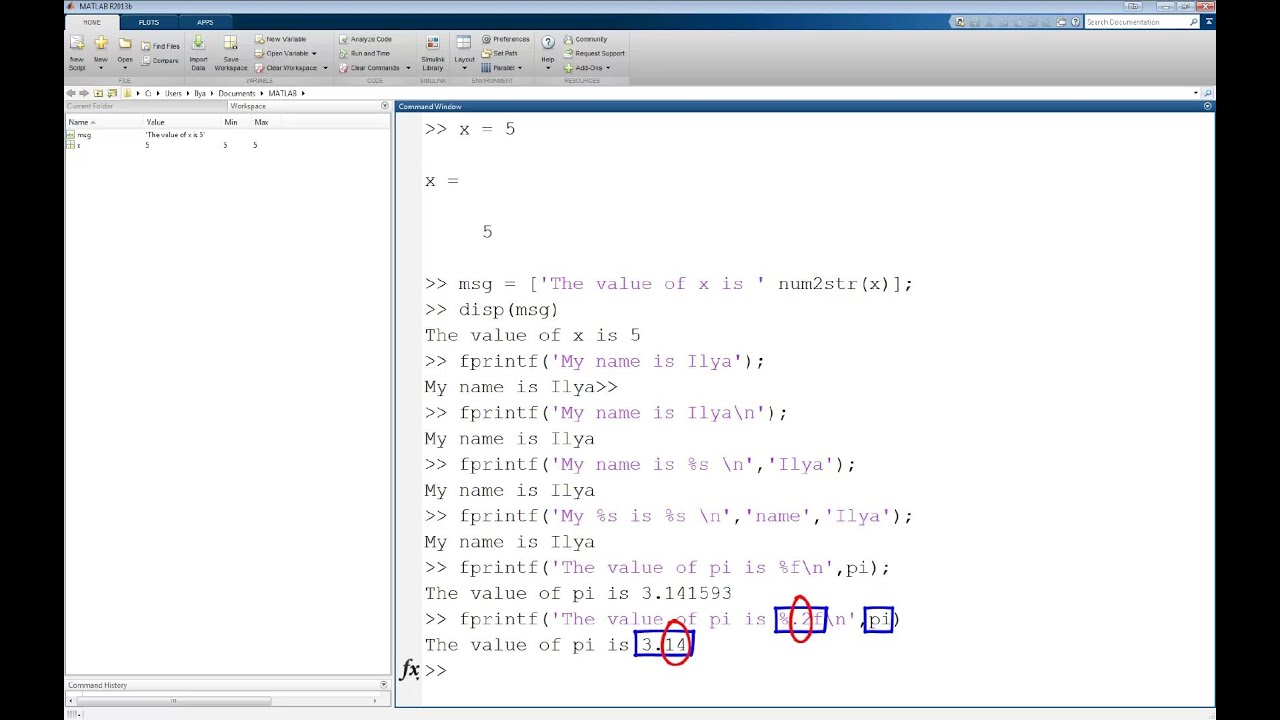
Fprintf (MATLAB Function Reference) MATLAB Function Referenceĭescription count = fprintf(fid, format,A.)įormats the data in the real part of matrix A (and in any additional matrix arguments) under control of the specified format string, and writes it to the file associated with file identifier fid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
